Accessing Uploaded Files - Apps & Notebooks
As described in Files Overview, file upload objects allow users to directly upload files into the cloud storage. This is useful for loading small files for experimentation and testing, especially for users without direct access to the cloud storage.
Once file upload objects have been created, the files are available in apps and notebooks to be ingested and utilized in testing and experiments.
File locations
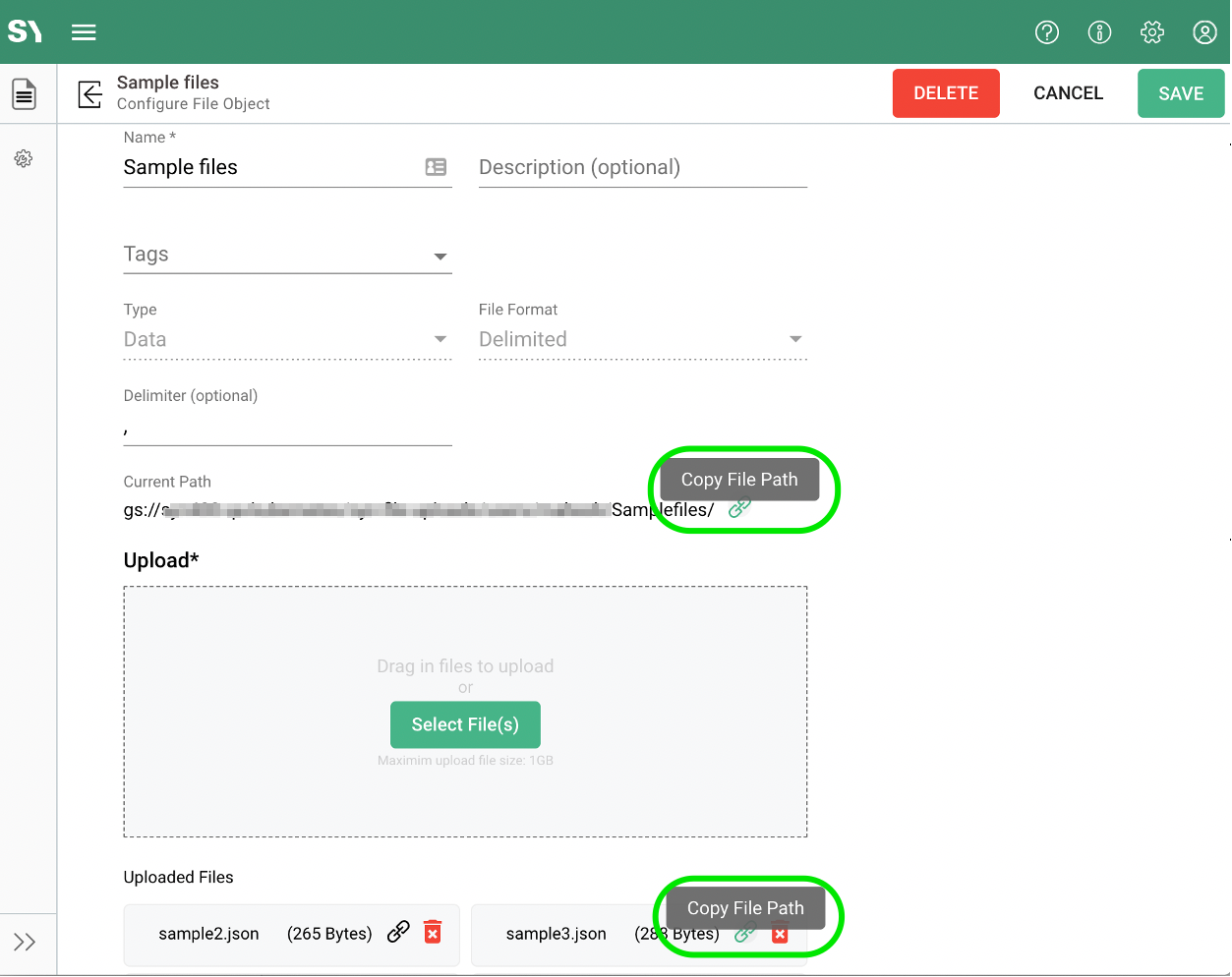
Whether using the upload files from an app or notebook, the mechanisms will require the file path and/or filename(s). The file path and path with the filename(s) can be copied via the copy link icon ( ) next to the path and files.
) next to the path and files.
Details
Use in Notebook
As explained in the Notebook Overview – SYNTASA™, Using Notebook within the Syntasa ecosystem, the needed tests and experiments can access the data available in the registered stores of the Syntasa platform. Following the steps in Creating a Notebook – SYNTASA™ redirects us to the Launching a Notebook – SYNTASA™, where we can write code and also utilize the Path basically configured in the File feature.
To use the files uploaded via the File feature in Notebooks, we just need to copy the FilePath as in the above screen and use this same path in the Notebook.
Files to upload GCP GCS bucket
Here is some sample code to help you get started reading files from Google Cloud Storage (GCS).
Path configured in the File feature can be utilized by copying and pasting it in the below piece of code in place of "path/to/your/file.Format".
from google.cloud import storage
import pandas as pd
# Set your GCS bucket and file paths
bucket_name = "your_bucket_name"
file_path = "path/to/your/file.Format"
# Initialize the GCS client
client = storage.Client()
# Get the GCS bucket
bucket = client.get_bucket(bucket_name)
# Get the blob (file) from the bucket
blob = bucket.blob(file_path)
# Download the blob's contents as a string
csv_content = blob.download_as_text()
# Create a pandas DataFrame from the CSV content
df = pd.read_csv(pd.compat.StringIO(csv_content))
# Now you can work with the pandas DataFrame (df)
print(df.head())
Files to upload AWS S3 bucket
Here is some sample code to help you get started reading files from Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3).
Path configured in the File feature can be utilized by copying and pasting it in the below piece of code in place of 'path/to/your/file.Format**.**
pip install boto3
import boto3
import botocore
# Define your AWS credentials and S3 bucket name
aws_access_key = 'YOUR_AWS_ACCESS_KEY'
aws_secret_key = 'YOUR_AWS_SECRET_KEY'
bucket_name = 'YOUR_S3_BUCKET_NAME'
file_key = 'path/to/your/file.Format' # Replace with the actual S3 file path
# Create an S3 client
s3 = boto3.client('s3', aws_access_key_id=aws_access_key, aws_secret_access_key=aws_secret_key)
try:
# Download the file from S3
s3.download_file(bucket_name, file_key, 'local_file.txt') # Saves the file locally as 'local_file.txt'
# Read the downloaded file
with open('local_file.txt', 'r') as file:
file_contents = file.read()
# Do something with the file contents
print(file_contents)
except botocore.exceptions.NoCredentialsError:
print("AWS credentials not found. Make sure to configure your AWS credentials.")
except botocore.exceptions.ClientError as e:
if e.response['Error']['Code'] == "404":
print(f"The object '{file_key}' does not exist in the S3 bucket.")
else:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
** Please remember to have authentication credentials to hand for GCS / S3.
* This is not the complete code, the complete code could vary as per the requirement.
There's a community Post as well to answer how a Notebook can access the file from Cloud buckets (files already uploaded through files).
Details
Use in Code Process.
Notebooks can't be dragged and dropped into the workspace canvas during creating the apps. we can still utilize the target files in dragging the code Process in the Appse.g., Spark processor.
To use the Files Code Process can be configured using the code mentioned in the above Section Use in Notebook and Code process.